Introduction
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach to identifying and addressing potential failures in products, processes, designs, or services. Widely used in Lean management, FMEA is an essential tool for risk assessment and quality improvement. It allows teams to anticipate possible points of failure and implement corrective actions proactively.
History and Development
The origins of FMEA can be traced back to the 1940s when it was developed by the U.S. military. It later found applications in the aerospace and automotive industries, especially within companies like NASA and Ford. Over time, FMEA has evolved into a key component of Total Quality Management and Lean methodologies.
Key Principles
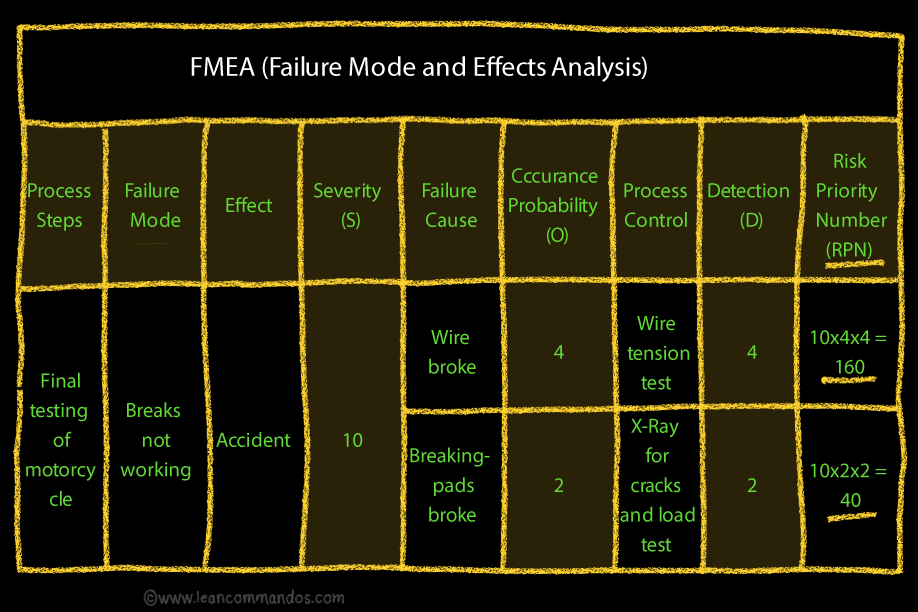
FMEA is grounded in the anticipation of failure modes (ways in which a process could fail), their effects (the impact of the failure), and their causes (reasons for the failure). It uses a systematic framework to rate each potential failure by its severity, occurrence, and detection, leading to a Risk Priority Number (RPN) that prioritizes risks for corrective action.
When to Use the Tool
FMEA is best utilized in the design phase of a product, process, or service, or when a new process is being implemented. It’s also effective when changes are made to existing processes, policies, or equipment, and when analyzing failures from customer feedback or quality control defects.

How It Works
Implementing FMEA involves several detailed steps, each designed to comprehensively analyze risk points and their mitigation. The first step is to assemble a cross-functional team with expertise relevant to the process under review. This team will create a list of every possible failure mode and the effects these failures could have on the end product or the customer.
Each failure mode is then rated on a scale, typically from 1 to 10, for three criteria: Severity (S), Occurrence (O), and Detection (D). Severity is the measure of how seriously the failure affects the customer, Occurrence assesses the frequency of the failure happening, and Detection evaluates the likelihood that the failure will be detected before reaching the customer. Multiplying these three numbers gives the Risk Priority Number (RPN):
RPN = S × O × D
The higher the RPN, the higher the risk, which necessitates prioritization for corrective measures. Actions to mitigate risks might include design changes, process modifications, enhanced quality control checks, or employee training.
After implementing these actions, the FMEA should be revisited to assess the effectiveness of the interventions, adjusting the ratings for Occurrence and Detection based on the new data. This makes FMEA an iterative process that continuously improves quality and safety.
Benefits
FMEA significantly lowers the chances of product or process failure, enhancing customer satisfaction and safety. It also reduces the costs associated with defects and fosters a proactive culture of risk management and continuous improvement within an organization.
Case Study
In the automotive industry, a manufacturer used FMEA when it identified a trend of engine overheating in one of its models. The FMEA revealed that a failure mode was a suboptimal coolant hose that could easily rupture. By redesigning the hose and altering the installation process, the manufacturer mitigated the risk, leading to a significant reduction in overheating incidents.
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls
Common mistakes in FMEA include incomplete analysis, ignoring low-risk areas that could become significant, and failing to take action on identified risks. Additionally, neglecting to revisit the FMEA after changes are made is a missed opportunity for continuous improvement.
Tips for Success
For FMEA to be successful, thoroughness is key. Encourage full team participation, ensure complete analysis, prioritize based on RPN, implement effective corrective actions, and regularly revisit the FMEA for updates and improvements.

FAQs
When should FMEA be conducted?
Ideally, during the design phase of a process or product and after any major changes or when issues are detected.
How often should FMEA be updated?
It should be reviewed regularly, especially after process changes, new quality data, or customer
feedback.
Who should be involved in the FMEA process?
A cross-functional team with diverse expertise related to the product or process being analyzed.
What is an acceptable RPN?
Acceptable RPN varies by industry and process. Prioritization should focus on the highest RPNs, but also consider the absolute values of S, O, and D.
Can FMEA eliminate all risks?
No, but it significantly reduces risks by prioritizing and mitigating the most critical ones.
Integration With Other Lean Tools
FMEA often works in tandem with other Lean tools like PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act), Root Cause Analysis, and Kaizen for continuous improvement and systematic problem-solving.
References and Further Reading
For those looking to deepen their understanding of FMEA and its application in Lean management, the following books are highly recommended:
- “The Basics of FMEA” by Robin E. McDermott, Raymond J. Mikulak, and Michael R. Beauregard. This book provides a foundational understanding of FMEAs and how to apply them effectively.
- “FMEA – Failure Mode and Effects Analysis” by Dyadem Press. A comprehensive guide that takes readers through the detailed process of conducting FMEAs.
- “Effective FMEAs: Achieving Safe, Reliable, and Economical Products and Processes using Failure Mode and Effects Analysis” by Carl S. Carlson. Carlson offers insights into making FMEAs more effective and provides case studies to illustrate best practices.
These resources offer in-depth knowledge and practical advice on effectively applying FMEA in various industrial contexts, thus serving as a valuable asset for professionals dedicated to quality and risk management.



7 Responses
I am always invstigating online for tips that can benefit me. Thanks!
I have been surfing online more than three hours as of late, yet I by no means discovered any fascinating article like yours. It¦s beautiful worth enough for me. In my view, if all website owners and bloggers made excellent content as you did, the net might be a lot more helpful than ever before.
Hi there, simply became alert to your weblog via Google, and found that it’s truly informative. I am going to be careful for brussels. I’ll be grateful for those who continue this in future. Lots of other folks shall be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Looking forward to reading more. Great article.Much thanks again. Really Cool.
hi!,I like your writing very much! share we keep up a correspondence extra about your article on AOL? I need a specialist on this house to solve my problem. Maybe that is you! Looking ahead to peer you.
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
Good – I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs as well as related info ended up being truly simple to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, site theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Excellent task..